An introduction to Internet of Things (IoT)
- December 29, 2017
- Posted by: Shachi Marathe
- Category: Big Data ,
This article will make you aware of the concept of Internet of Things. As the title of the article suggests, it is just an introduction of the concept and will briefly touch upon the various aspects of Internet of Things, its history, uses, applications, future and constraints.
Shachi Marathe introduces you to the concept of Internet of Things, more commonly known as IoT. The article takes you through the concept of IoT, its application and uses, potential and future and of IoT. The article will also delve into constraints and criticisms.
Key Concepts
Internet of Things is a concept that is fast evolving. With the World getting connected via the Internet, Internet is now, a way of life. We need the Internet for all our basic needs as well, say for grocery shopping, managing bank accounts, managing travel arrangements, the list is endless. Most of the devices (“things”) that we use on a daily basis are controlled by remotes and at times by applications on our mobile devices. This has led to a “network” of its own and it is commonly called as “Internet of Things”.
Subscribe Now
By reading this article you will learn:
- What is the Internet?
- What is IoT?
- History of IoT
- How IoT works?
- Few applications of IoT
- The future and potential of IoT
- Technological challenges of IoT
- Criticisms and controversies
What is the Internet?
The Internet, commonly called the “Net”, is a system of interconnected computer networks. This network, allows sharing of resources and information, based on appropriate permissions.
In today’s world, the Net is primarily responsible for making it possible to get all kinds of information from anywhere in the world, at our fingertips, no matter where we are, as long as we have “connectivity”.
What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
Internet of Things (IoT) in the simplest of terms is a network of “things” or objects, which have embedded software, such that it enables these “things” to “talk” to each other or “connect” with each other and exchange data.
IoT is based on the technology, where objects have inbuilt sensors or applications, and are connected over an existing network, which further enables integration between these systems, giving us improved accuracy and efficiency, which further leads to improved lifestyle and economic benefits.
To give a day-to-day example, we have temperature controlled rooms, which adjust their temperature based on the temperature outside, or we have microwaves that can be controlled from smart phones. In both cases, Devices communicate with each other through the internet to perform specific actions based on collected information.
History of IoT
The phase, “Internet of Things” (IoT) was first coined in 1999 by Kevin Ashton, the Executive Director of Auto-ID Labs at MIT during his speech at Procter & Gamble. He was of the opinion that RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) was an important factor to link and tag devices to then track and manage data.
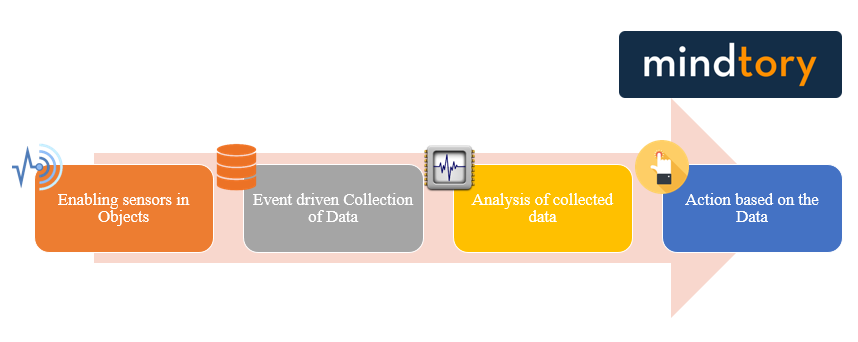
How IoT works?
IoT (Internet of Things) is not a technology in itself. It is a union of multiple technologies that work together to seamlessly bridge the gap between the physical and virtual worlds, finally leading to increased efficiency and accuracy of data collection and as a result, data processing and information. There is minimum human intervention, as it is a direct integration of machines and technology. Devices are embedded with “chips” that “read” data based on certain impulses, these could be say a change in temperature, a change in movement, location, or just plain, simple, pre-decided, time intervals. These sensors and chips are then connected to an IoT platform. This platform then collects and integrates data that is collected from these various devices. Based on the algorithmic applications and data analyzing applications, collected data is then checked for patterns, trends and other valuable information. This can then be used to resolve issues, solve problems or improve business.
Applications of Internet of Things (IoT)
As this article deals with a basic introduction to IoT, we have documented some basic applications of IoT. There are many more areas in which Internet of Things is used and can be used in the future, so this list here is not an exhaustive list of Applications. IoT is used by us, consumers or normal users, as well as by larger industries and Government Organizations.
Consumer Applications
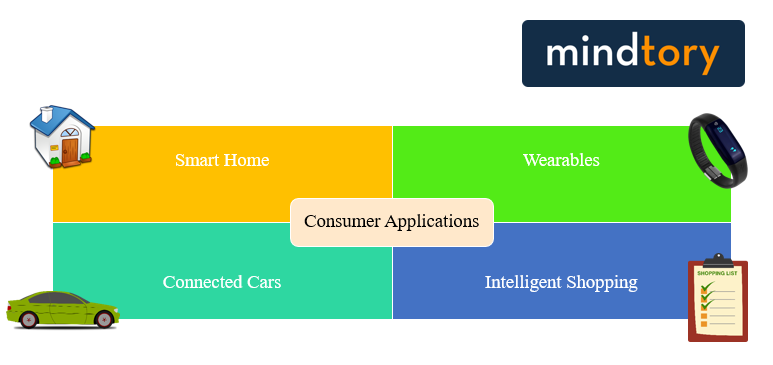 We are the consumers and we are connected to the Internet via various devices; our television sets, our smart phones, watches and many more.
We are the consumers and we are connected to the Internet via various devices; our television sets, our smart phones, watches and many more.
Smart Homes – Our homes are now equipped with various devices like Smart TVs, Smart electrical systems, entertainment systems and other appliances like the refrigerator, washing machines, dish washers, ovens, the list is endless. Consumers get ease of use and in the long term a more environmentally friendly abode. In some homes, we can even turn on or off devices via applications on our phones. However, for plumbing and other such services can be got by Sarkinen Plumbing list of services. This is taking IoT to a higher level than simple “smart” features.
Wearables – Now that we have technology that we can wear, we can safely say that we are using IoT. Our watches, our fitness bands, are all examples of IoT.
Connected Cars – Cars now have inbuilt GPS, automated gear changing systems, temperature control, lighting control. All these are forms of usage of IoT. RFIDs on cars are used at toll plazas, entry and exit gates, making it more technology dependent and less human dependent.
Intelligent Shopping – You must have noticed that if you shop online, or browse online, you are given tips on what you may want to buy, what others are buying and then nudging you towards making a choice. Now, how does this happen? This is based on the data collected based on your browsing history, your location, your shopping history, likes and dislikes on social media, etc and analysis of the same. The effect is that, you feel better about shopping because you think you are looked after. Also, you may be coaxed into buying things that you otherwise would have skipped. So, this leads to further sales for the company.
Other areas and applications of use are –
- Information Media – Targeting users based on the news programs that they watch and browse. This provides users with information that they want to be easily accessible without too much of searching.
- Transportation – Digital signs, digital parking, are all applications related to IoT. These can then gather data and let required authorities know about congestions on roads, opportunities for improvement, etc.
- Manufacturing – Controlling of production lines, supply chain networks, prediction of demands, inventory are all made easy with IoT. This leads to increase in output, lesser chance of human error and finally, more profits.
- Agriculture and environmental monitoring – Agriculture is dependent to a large scale on climatic conditions. With a lot of study being put into climate change, studying the environment, temperature conditions, rainfall conditions, it is getting easier to predict and then manipulate agricultural cycles. Though it cannot be completely fool proof because nature is unpredictable, it does help to a large extent to avoid or curtail losses. All this is possible because of the data collected using IoT. Devices are placed on farms. Data related to moisture in the soil, nutrients, water table, can all be collected and based on data collected, farmers can get a better yield from the land, thus leading to more profits. Monitoring the environment is also easier and this helps in more accurate prediction of natural calamities, which in turns helps in saving more lives.
- Smart Cities – As the name suggests, now our cities, the areas we live in will become “Smart”, rather quite a bit of them are already “smart”. There is smart and automated transport systems, security systems are connected and more sophisticated. Energy management systems are not far behind, nor are water distribution systems. All this leads to better living conditions. Tickets can be pre-booked, parking slots can be pre-booked and this leads to more hassle free living space.
- Healthcare – Though much has not yet been implemented in healthcare in terms of connectivity and IoT, there is a huge potential in this field. The data that is collected will then enable doctors and care givers to provide more accurate and personalized treatment to the individual. Not only will it make easier, but also make it a more pleasant experience.
- Energy Grid management – Smart grids are gaining popularity across the world. The basic premise of smart grids is to collect data automatically. This data will provide an insight into the behavior of electricity consumers. This can then lead to improvement in efficiency of supply systems, leading to saving of electricity.
There are many more such applications and the more you think of it, the deeper we can go.
Future and Potential of IoT
With digital transformation, and the progress of IoT we will be using IoT in nearly every aspect of existence. BI Intelligence has estimated that by 2020, on our planet, there will be more than 24 billion devices connected by and using IoT.
IoT will form a major chunk of the way in which the World operates and connects with each other.

Technological challenges of IoT
Though IoT has a lot of potential and the future is bright, there are many technological challenges that need to be overcome before it can reach its true potential.
Some of the challenges that are currently being faced are –
- Scalability of existing infrastructure – The existing infrastructure will definitely be unable to manage the growing need of connectivity. IoT needs a more robust infrastructure if it has to grow as envisaged.
- Standardization of technology that is used for IoT – Currently, there are various platforms and service providers, which provide services for IoT. There are many companies which manufacture devices. Currently, there is no standardization of the technology being used for all this and when it is time to integrate or further link devices or share data, IoT may run into hurdles.
- Complexity of software required to process data – The software that is used to analyze the large volumes of data is complex. It requires scientific computations, because without these complex algorithms and processes, all the data that is collected will be of no use.
- Sheer volume of data that is generated and analysis of these data – We know by now that we have a large population that is connected to the Internet. In doing so, all of us are generating lots of data. Even all of us who are reading this have generated Now, some of it is useful and some of it is sheer junk. Sorting through this data and getting meaningful results is a herculean task. If this process is faulty, the results will be faulty as well. So, if the results are inaccurate, naturally businesses as well as applications that use these data will be inaccurate or will fail.
Criticisms and controversies
As with any other discovery, IoT also has its share of criticisms. Considering the fact that IoT is used for personal devices, personal data is out on the public domain. The same holds true for corporate data. So, the main threat and concern is of misuse of data by miscreants. So, privacy and security of data is a primary concern.
The next aspect is, who is the owner of all this data? Consider the data collected by a Corporate or by the Government, is primarily data related to users or citizens; so does this data belong to the users or to the corporate? So, effectively, who controls the data? Thus, autonomy and control of data being collected is a point of concern.
One more important aspect is interpretation of data. Data analytics and algorithms related to the same are basically written by humans, and their understanding of the subject. So, there is a chance that the premise of these algorithms is incorrect. Also, if everything is mechanical, the human touch that is required to analyze more complex issues, or issues that maybe outside the purview of just data may not be addressed effectively.
Conclusion
IoT is a relatively new concept, which is catching on fast. Usefulness of IoT is for everyone to see and Corporates are using IoT for data analytics and increasing their reach and profit margins. IoT as a concept is here to stay, despite its criticisms and technological challenges.
References
- http://www.dataversity.net/brief-history-internet-things/
- http://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/definition/Internet-of-Things-IoT
- http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6005163/
- https://www.happiestminds.com/Insights/internet-of-things/
- https://iot-analytics.com/10-internet-of-things-applications/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things
- https://www.forbes.com/forbes/welcome/?toURL=https://www.forbes.com/sites/jacobmorgan/2014/05/13/simple-explanation-internet-things-that-anyone-can-understand/&refURL=https://www.google.co.in/&referrer=https://www.google.co.in/
- https://www.slideshare.net/jaswindersinghthind/a-basic-ppt-on-internet-of-thingsiot
Subscribe now
Subscribe now and get weekly free news letters and access to many free articles, researches and white papers. You can subscribe by creating your account or by entering your e-mail address in the following subscribe text box.

